
Lipoprotein(a) has proven to be a causal factor of MI not just a risk marker for cardiovascular disease. European doctors are now systematically screening all their patients for LPA in addition to HDL and LDL, Private wellness laboratories in the United States are also targeting LPA in their risk assessment profile.
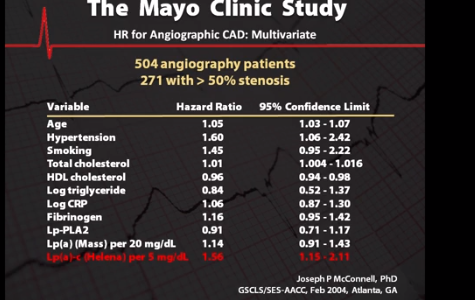
Several landmark studies have precipitated this shift, researchers at the Mayo Clinic studied the cardiac and geographies of 507 patients and found LPA cholesterol to be the single best predictor of coronary artery disease. In a June 2009 study of over 41,000 patients, researchers at Copenhagen University found that those with the top 10% of LPA levels had 2-3 times the incidence of MI. At the University of Oxford researchers found 1 in 6 people of European descent have specific genotypes that result in high LPA levels and an elevated risk of heart disease. This risk was independent of high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking and other known risk factors.
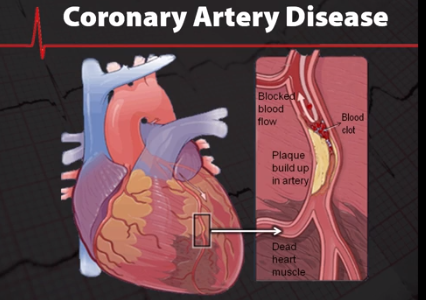
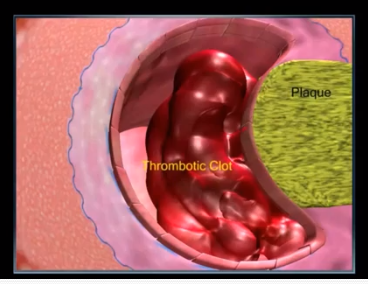
LPA and other lipoproteins cause heart disease by increasing plaque deposits in coronary arteries. Plaque is a fatty arterial lesion that generally develops over a period of many years. Plaque development is complex but we know that lipoprotein particles like LPA penetrate the intimal space of arterial cellular membranes that have been weakened by hypertension like oscillation, nicotinic DNA damage and other factors. Over time plaque may weaken and rupture triggering thrombosis that can result in an atherothrombotic clot, if the blockage in the artery is big enough it causes an acute ischemic event like a heart attack or even death.
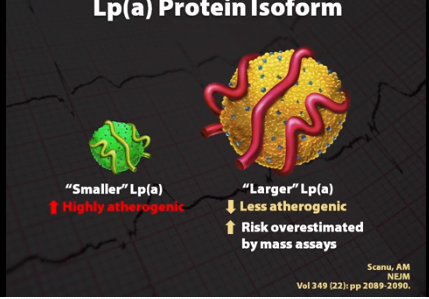
LPA can be assessed several ways immunoassays or mass assays measure the protein content of LPA, but due to the complex nature of LPA mass assays have not been found to be highly relevant. To date 53 different sized LPA's have been identified, larger LPA protein molecules are less atherogenic than smaller LPA molecules. Unfortunately, mass assays tend to overestimate LPA and coronary risk when larger isoforms are present. Even worse risk may be underestimated when small highly atherogenic molecules are present.
Fortunately, LPA can be measured by its cholesterol content with much greater diagnostic value, the LPA cholesterol assay by Helena has proven to be the single best predictor of both plaque development and major ischemic events. Researchers from the Mayo Clinic have confirmed that LPA cholesterol measurement is superior to mass LPA for predicting heart disease. Identifying and treating those with high LPA is crucial to reducing heart disease. Niacin and statins have been shown effective in treating elevated LPA levels and for entirely new LPA drugs are in development. Researchers at Harvard have studied 27,000 healthy women and found that hormone replacement therapy can reduce the risk of cardiac disease in postmenopausal women with high LPA.
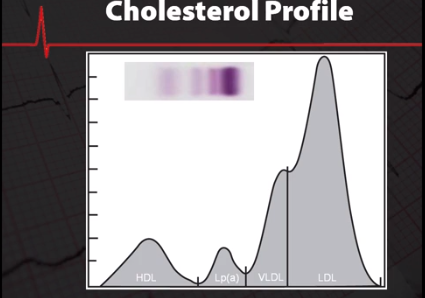
The facts are clear, everyone should be tested by the Helena LPA cholesterol method to accurately evaluate the risk for early heart disease, patients with an elevated LPA should be checked every 3-6 months to monitor therapeutic progress. The Helena LPA assay is easy to do with standard electrophoresis equipment. Please give us a call if you are interested in setting up this procedure.
Watch the full video version from Helena Laboratories here:
Want to check our products and accessories from Helena Laboratories? Visit the links below!